Background:
This post continues a comparison of results using an open intake versus a closed intake.
Setup:
The closed intake is from Eventuri and the open intake is the Eventuri, minus the front portion that seals with the GTI grill. The GTI is equipped with an IS38+ turbocharger tuned to produce 28 psi upon boost onset and tapering to approximately 25 psi.


Many open style intakes use a partition to try and keep the engine compartment air from being ingested by the air filter. For this test the setup simulates an open intake that doesn’t have a partition – or one that does a poor job.
Test Procedure:
This test will consist of a single third gear full throttle pull to above 6,000 RPM. The purpose is to find what difference there is in intake air temperatures and work required from the turbocharger.
Test Results:
Data from using the Closed intake are shown in the chart:
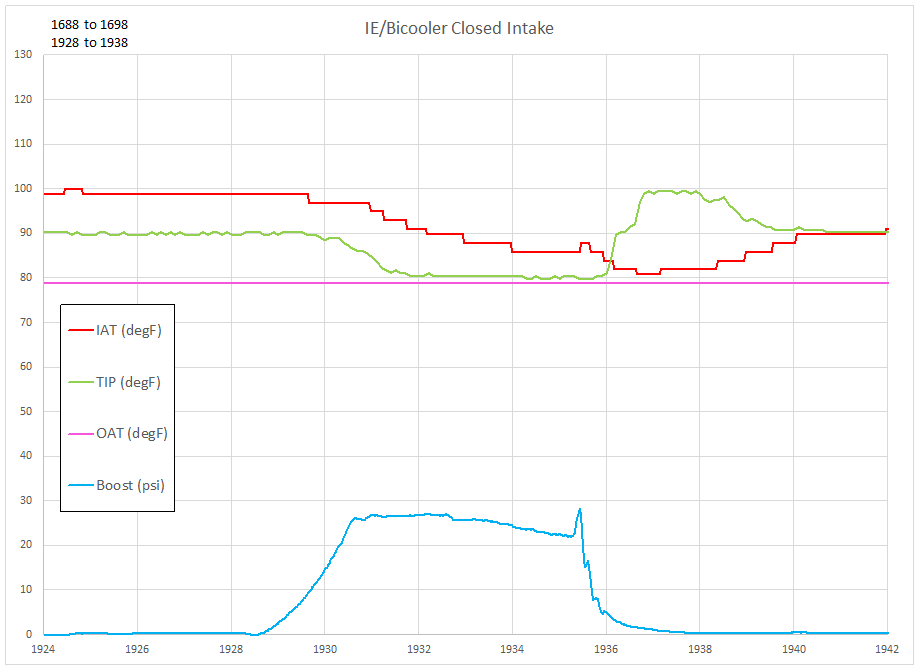
Prior to the pull the air temperature going into the turbocharger (TIP) is approximately 10-12 degF above the outside air temperature (OAT). The IAT is about 20 degF above the outside air temperature. During the pull both temperatures decrease, with the air temperature into the turbo decreasing to approximately 2 degF above the outside air temperature.
Next the Open intake configuration is setup. The results are shown on the chart:
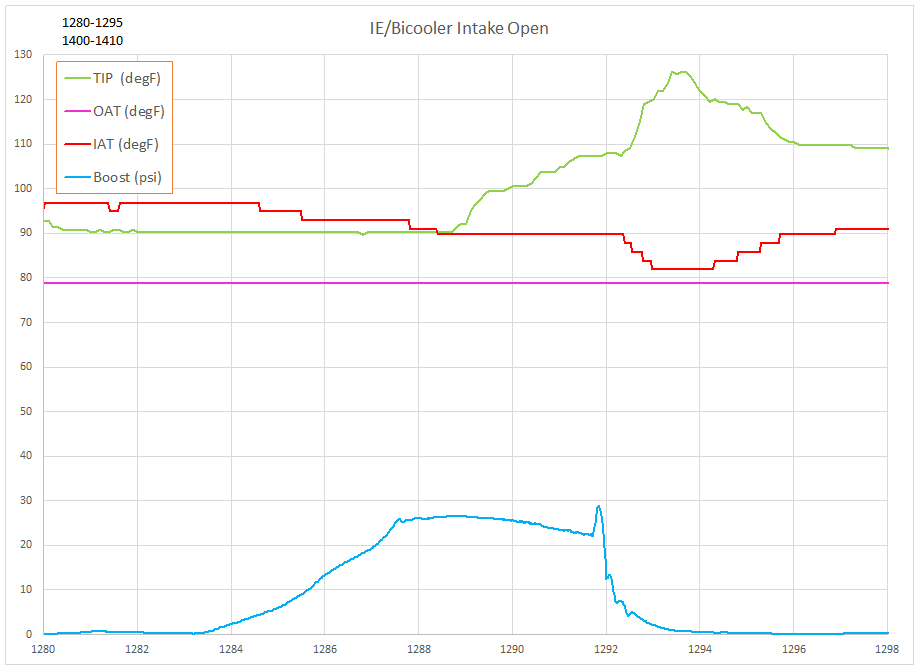
Prior to the pull the air temperature into the turbocharger is approximately 12 degF above the outside air temperature. The IAT is approximately 18 degF above the outside air temperature. During the pull the temperature into the turbocharger begins to increase while the IAT decreases and then levels off.
The next chart overlays data from each test case. The closed intake is shown with dashed lines and the open intake is shown with solid lines.
Note: Multiple pulls were made for each test setup.

Outside air temperature is the same for both and is the straight line on the chart. The IAT between test cases differs from approximately 2-4 degF. Most interesting is the change in the turbocharger wastegate duty cycle (WGDC), an indicator of how much exhaust gas is being directed through the turbine versus bypassing the turbine.
The WGDC is roughly, on average, about 10 percent higher with the Open intake versus the Closed intake.
Conclusion:
Comparison of an Open intake versus Closed intake shows that the turbocharger wastegate duty cycle during a third gear pull is approximately 10% higher for the Open intake when using an IS38+ turbocharger boosting to 25-28 psi.

So in the conclusion is the open intake or closed intake “better”? I’m not sure if more duty cycle is good or bad so to speak…
Yes, I’m not exactly understanding the duty cycle and how it relates to more/less boost and more/less work by the turbo (having to spin faster to make the same amount of boost).
More duty cycle is a request by the ECU to have more exhaust gas go through the turbine than bypass it through the wastegate port. That extracts more energy from the exhaust to drive the compressor wheel, but increases the pressure going into the turbine. The elevated turbine inlet pressure negatively affects the exhaust gas exiting the cylinder because the exhaust is exiting into a higher pressure region than if more exhaust gas bypassed the turbine. The end result is a decrease in engine volumetric efficiency. I have no idea what the scale of the impact is, but higher duty cycle is not beneficial in this case.
Boost also appears to come on faster with the closed intake.which is weird, would have thought the open intake would allow it to hit boost faster. I suppose with ingesting the hotter air it takes longer to hit the boost target which matches with the wastegate duty cycle needing to be higher. It has to pump more hot air to reach the target boost post inter cooler. Sound correct?
I’d need to go back and check to see if I pressed the accelerator at the same engine rpm, I probably did not since I wasn’t intending to compare boost onset when I recorded this data. For a boost onset comparison I prefer to collect about a dozen data points for each test case.